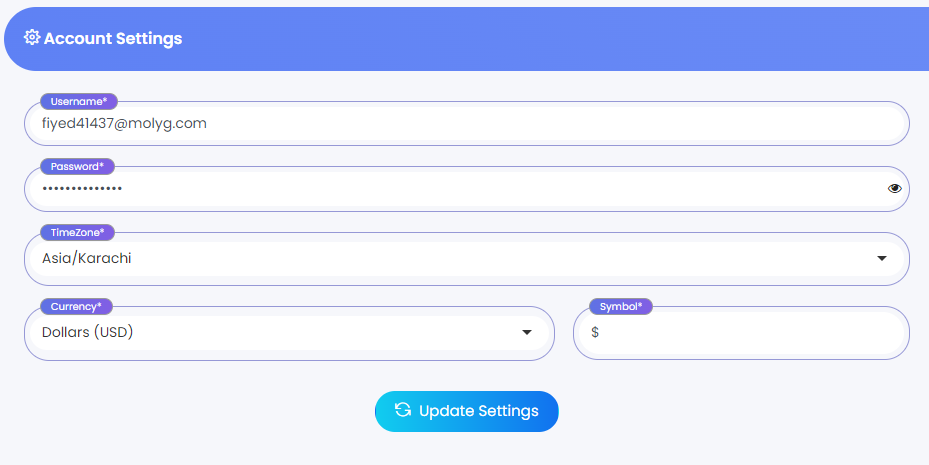
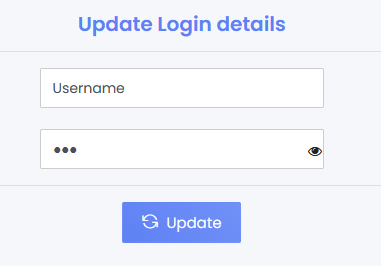
Eskooly application's current process for updating passwords is insufficiently secure, as it only requires users to enter a new password and its confirmation, without asking for the current (old) password.
Broken Authentificaton
Weak password
Brute Force
Inadequate Password Update Verification
Update Admin password
Update Teacher/Student
High.
Given that the application hold critical and sensitive data, the impact of this vulnerability is extremely High. Successful exploitation allows attackers full access to all stored credentials, leading to potential identity theft and unauthorized access to various services. The ability to change passwords without the original one could lead to account takeovers and significant data breaches.
High.
The likelihood is medium because to exploit this vulnerability, the attacker must have access to the victim's current session, e.g. the victim has left his browser session open. The attacker will therefore be able to modify the victim's password without knowing the original.
It is recommended to enhance the password update process by requiring users to input their current password before setting a new one. This step adds a crucial verification layer to ensure that only authorized users can change passwords.