Active exploitation of TP-Link, Apache and Oracle vulnerabilities detected
Date: 02-05-2023

The US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has updated the Catalog of Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) with three new vulnerabilities, due to evidence of ongoing exploitation.
Identified security vulnerabilities include:
CVE-2023-1389 (score CVSS : 8,8) - TP-Link Archer AX-21 Command Injection Vulnerability
CVE-2021-45046 (score CVSS : 9,0) - Apache Log4j2 Deserialization of Untrusted Data Vulnerability
CVE-2023-21839 (score CVSS : 7,5) - Oracle WebLogic Server Unspecified Vulnerability
CVE: The acronym CVE, for Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures in English, designates a public list of computer security vulnerabilities. When we talk about a CVE, we generally refer to a security vulnerability that has been assigned a CVE identifier.
Security advisories published by vendors and researchers almost always mention at least one CVE identifier. CVEs help professionals coordinate their efforts to prioritize and resolve vulnerabilities, and thus strengthen the security of computer systems.
SOURCE: REDHAT
CVE-2023-1389 concerns a command injection vulnerability affecting TP-Link Archer AX-21 routers, which could be exploited to enable remote code execution. Trend Micro's Zero Day Initiative reported that since April 11, 2023, malicious actors associated with the Mirai botnet have been actively exploiting this vulnerability.
The second vulnerability added to the KEV catalog is CVE-2021-45046, which concerns remote code execution in the Apache Log4j2 logging library, discovered in December 2021.
An article is available from Be-Hacktive: => LOG4J: The vulnerable bookstore that is shaking the planet
Exactly how this specific vulnerability is exploited is not yet clear. However, GreyNoise has collected data indicating exploitation attempts from as many as 74 unique IP addresses over the past 30 days. This also includes CVE-2021-44228 (also known as Log4Shell).
An article is available from Be-Hacktive:
=> LOG4SHELL: COME, SEE, LIVE
The latest addition to the list is a high-severity bug found in Oracle WebLogic Server versions 12.2.1.3.0, 12.2.1.4.0, and 14.1.1.0.0, which could potentially allow unauthorized access to sensitive information . Oracle released fixes for this issue in January 2023.
“Oracle WebLogic Server contains an unspecified vulnerability that allows an unauthenticated attacker with network access via T3, IIOP, to compromise Oracle WebLogic Server,” CISA said.
Although proof-of-concept (PoC) exploits for the flaw exist, there do not appear to be any public reports of malicious exploitation.
Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies are required to implement vendor-provided patches by May 22, 2023, to protect their networks against these active threats.
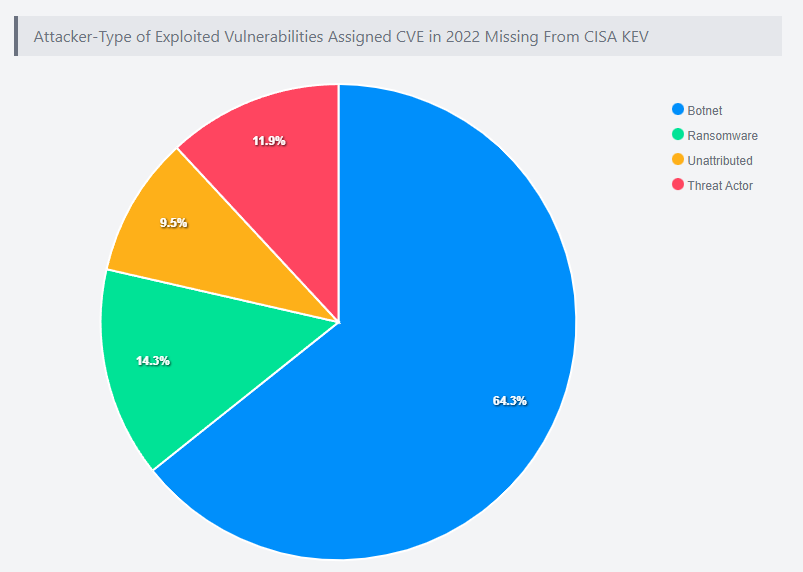
This recommendation comes just over a month after VulnCheck revealed that nearly four dozen security vulnerabilities, likely used as weapons in the wild in 2022, are missing from the KEV catalog.
Among the 42 vulnerabilities, an overwhelming majority are linked to exploitation by botnets similar to Mirai (27), followed by ransomware gangs (6) and other threat actors (9).
Last updated